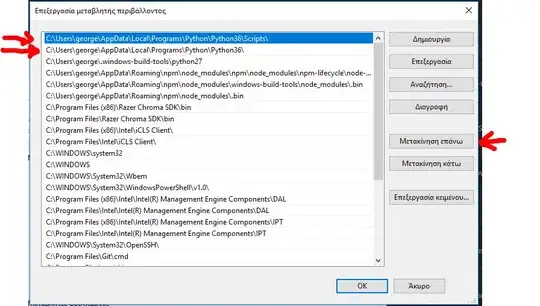
So I took a look at the link and the table you're trying to get.
The problem with the table in the link is that it contains multiple headers so the .read_html(URL) function, gets all of them and sets those as your
header:
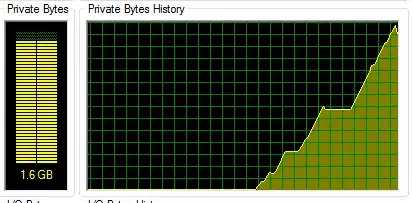
so instead of using pandas to read the HTML I used
beautiful soup for what you're trying to accomplish.
With beautiful and urllib.requests I got the HTML from the URL and extracted the HTML with the table class name
url = "https://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/topics/animals-and-plants/threatened-species/programs-legislation-and-framework/nsw-koala-strategy/local-government-resources-for-koala-conservation/north-coast-koala-management-area#:~:text=The%20North%20Coast%20Koala%20Management,Valley%2C%20Clarence%20Valley%20and%20Taree."
#load html with urllib
html = urllib.request.urlopen(url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(html.read(), 'lxml')
#get the table you're trying to get based
#on html elements
htmltable = soup.find('table', { 'class' : 'table-striped' })
Then using a function I found to make a list from tables extract from beautiful soup, I modified the function to get your values in a shape that would be easy to load into a dataframe and would also be easy to call depending on what you want:
[{"common name" : value, "Species name": value, "type": value}...{}]
def tableDataText(table):
"""Parses a html segment started with tag <table> followed
by multiple <tr> (table rows) and inner <td> (table data) tags.
It returns a list of rows with inner columns.
Accepts only one <th> (table header/data) in the first row.
"""
def rowgetDataText(tr, coltag='td'): # td (data) or th (header)
return [td.get_text(strip=True) for td in tr.find_all(coltag)]
rows = []
trs = table.find_all('tr')
headerow = rowgetDataText(trs[0], 'th')
if headerow: # if there is a header row include first
trs = trs[1:]
for tr in trs: # for every table row
#this part is modified
#basically we'll get the type of
#used based of the second table header
#in your url table html
if(rowgetDataText(tr, 'th')):
last_head = rowgetDataText(tr, 'th')
#we'll add to the list a dict
#that contains "common name", "species name", "type" (use type)
if(rowgetDataText(tr, 'td')):
row = rowgetDataText(tr, 'td')
rows.append({headerow[0]: row[0], headerow[1]: row[1], 'type': last_head[0]})
return rows
then when we convert the results of that function using
the table content we extracted with beautiful soup we get this:

Then you can easily reference the type of use and each value common/species name.
Here is the full code:
import pandas as pd
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import urllib.request
url = "https://www.environment.nsw.gov.au/topics/animals-and-plants/threatened-species/programs-legislation-and-framework/nsw-koala-strategy/local-government-resources-for-koala-conservation/north-coast-koala-management-area#:~:text=The%20North%20Coast%20Koala%20Management,Valley%2C%20Clarence%20Valley%20and%20Taree."
#load html with urllib
html = urllib.request.urlopen(url)
soup = BeautifulSoup(html.read(), 'lxml')
#get the table you're trying to get based
#on html elements
htmltable = soup.find('table', { 'class' : 'table-striped' })
#modified function taken from: https://stackoverflow.com/a/58274853/6297478
#to fit your data shape in a way that
#you can use.
def tableDataText(table):
"""Parses a html segment started with tag <table> followed
by multiple <tr> (table rows) and inner <td> (table data) tags.
It returns a list of rows with inner columns.
Accepts only one <th> (table header/data) in the first row.
"""
def rowgetDataText(tr, coltag='td'): # td (data) or th (header)
return [td.get_text(strip=True) for td in tr.find_all(coltag)]
rows = []
trs = table.find_all('tr')
headerow = rowgetDataText(trs[0], 'th')
if headerow: # if there is a header row include first
trs = trs[1:]
for tr in trs: # for every table row
#this part is modified
#basically we'll get the type of
#used based of the second table header
#in your url table html
if(rowgetDataText(tr, 'th')):
last_head = rowgetDataText(tr, 'th')
#we'll add to the list a dict
#that contains "common name", "species name", "type" (use type)
if(rowgetDataText(tr, 'td')):
row = rowgetDataText(tr, 'td')
rows.append({headerow[0]: row[0], headerow[1]: row[1], 'type': last_head[0]})
return rows
#we store our results from the function in list_table
list_table = tableDataText(htmltable)
#turn our table into a DataFrame
dftable = pd.DataFrame(list_table)
dftable
I left some comments for you in the code to help you out.
I hope this helps!