I am part of a team building a new Content Management System for our public site. I'm trying to find the easiest and best way to build-in a Revision Control mechanism. The object model is pretty basic. We have an abstract BaseArticle class that includes properties for version independent/meta data such as Heading & CreatedBy. A number of classes inherit from this such as DocumentArticle which has the property URL that will be a path to a file. WebArticle also inherits from BaseArticle and includes the FurtherInfo property and a collection of Tabs objects, which include Body that will hold the HTML to be displayed (Tab objects do not derive from anything). NewsArticle and JobArticle inherit from WebArticle. We have other derived classes, but these provide enough of an example.
We come up with two approaches to persistence for Revision Control. I call these Approach1 and Approach2. I've used SQL Server to do a basic diagram of each:
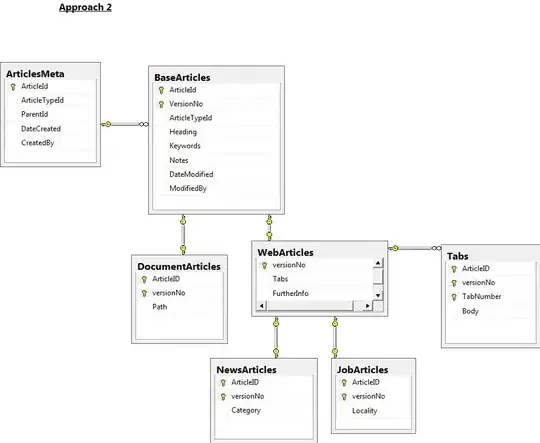
- With Approach1, the plan would be for fresh versions of
Articlesto be persisted via a database Update. A trigger would be set for updates and would insert the old data in to thexxx_Versionstable. I think a trigger would need to be configured on every table. This approach does have the advantage that the only theheadversion of each article is held in the main tables, with old versions being hived off. This makes it easy to copy the head versions of articles from the development/staging database to the Live one. - With Approach2, the plan would be for fresh versions of
Articlesto be inserted into the database. The head version of articles would be identified through views. This seems to have the advantage of fewer tables and less code (e.g. not triggers).
Note that with both approaches, the plan would be to call an Upsert stored procedure for the table mapped to the relevant object (we must remember to handle the case of a new Article being added). This upsert stored procedure would call that for the class from which it derives e.g. upsert_NewsArticle would call upsert_WebArticle etc.
We are using SQL Server 2005, although I think this question is independent of database flavor. I've done some extensive trawling of the internet and have found references to both approaches. But I have not found anything which compares the two and shows one or the other to be better. I think with all the database books in the world, this choice of approaches must have arisen before.
My question is: which of these Approaches is best and why?