printf("m=%d,M=%d,float_size=%d\n", m, M, floatsize);
a = (float*)malloc(floatsize * m * M);
f = (float*)malloc(floatsize * M);
printf("bytes of a is %d, bytes of f is %d\n", sizeof(a), sizeof(f));
The result is:
m=1,M=3,float_size=4
bytes of a is 8, bytes of f is 8
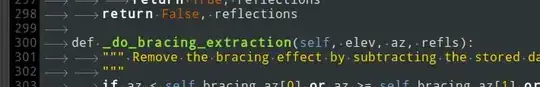
As screenshot shown below:
Shouldn't it be 3*4=12 instead of 8? How come?