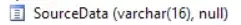I have created a simple way of finding offending fields by:
- Getting the column width of all the columns of a table where we're trying to make this insert/ update. (I'm getting this info directly from the database.)
- Comparing the column widths to the width of the values we're trying to insert/ update.
Assumptions/ Limitations:
The column names of the table in the database match with the C# entity fields. For eg: If you have a column like this in database:
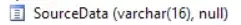
You need to have your Entity with the same column name:
public class SomeTable
{
// Other fields
public string SourceData { get; set; }
}
You're inserting/ updating 1 entity at a time. It'll be clearer in the demo code below. (If you're doing bulk inserts/ updates, you might want to either modify it or use some other solution.)
Step 1:
Get the column width of all the columns directly from the database:
// For this, I took help from Microsoft docs website:
// https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/system.data.sqlclient.sqlconnection.getschema?view=netframework-4.7.2#System_Data_SqlClient_SqlConnection_GetSchema_System_String_System_String___
private static Dictionary<string, int> GetColumnSizesOfTableFromDatabase(string tableName, string connectionString)
{
var columnSizes = new Dictionary<string, int>();
using (var connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
// Connect to the database then retrieve the schema information.
connection.Open();
// You can specify the Catalog, Schema, Table Name, Column Name to get the specified column(s).
// You can use four restrictions for Column, so you should create a 4 members array.
String[] columnRestrictions = new String[4];
// For the array, 0-member represents Catalog; 1-member represents Schema;
// 2-member represents Table Name; 3-member represents Column Name.
// Now we specify the Table_Name and Column_Name of the columns what we want to get schema information.
columnRestrictions[2] = tableName;
DataTable allColumnsSchemaTable = connection.GetSchema("Columns", columnRestrictions);
foreach (DataRow row in allColumnsSchemaTable.Rows)
{
var columnName = row.Field<string>("COLUMN_NAME");
//var dataType = row.Field<string>("DATA_TYPE");
var characterMaxLength = row.Field<int?>("CHARACTER_MAXIMUM_LENGTH");
// I'm only capturing columns whose Datatype is "varchar" or "char", i.e. their CHARACTER_MAXIMUM_LENGTH won't be null.
if(characterMaxLength != null)
{
columnSizes.Add(columnName, characterMaxLength.Value);
}
}
connection.Close();
}
return columnSizes;
}
Step 2:
Compare the column widths with the width of the values we're trying to insert/ update:
public static Dictionary<string, string> FindLongBinaryOrStringFields<T>(T entity, string connectionString)
{
var tableName = typeof(T).Name;
Dictionary<string, string> longFields = new Dictionary<string, string>();
var objectProperties = GetProperties(entity);
//var fieldNames = objectProperties.Select(p => p.Name).ToList();
var actualDatabaseColumnSizes = GetColumnSizesOfTableFromDatabase(tableName, connectionString);
foreach (var dbColumn in actualDatabaseColumnSizes)
{
var maxLengthOfThisColumn = dbColumn.Value;
var currentValueOfThisField = objectProperties.Where(f => f.Name == dbColumn.Key).First()?.GetValue(entity, null)?.ToString();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(currentValueOfThisField) && currentValueOfThisField.Length > maxLengthOfThisColumn)
{
longFields.Add(dbColumn.Key, $"'{dbColumn.Key}' column cannot take the value of '{currentValueOfThisField}' because the max length it can take is {maxLengthOfThisColumn}.");
}
}
return longFields;
}
public static List<PropertyInfo> GetProperties<T>(T entity)
{
//The DeclaredOnly flag makes sure you only get properties of the object, not from the classes it derives from.
var properties = entity.GetType()
.GetProperties(System.Reflection.BindingFlags.Public
| System.Reflection.BindingFlags.Instance
| System.Reflection.BindingFlags.DeclaredOnly)
.ToList();
return properties;
}
Demo:
Let's say we're trying to insert someTableEntity of SomeTable class that is modeled in our app like so:
public class SomeTable
{
[Key]
public long TicketID { get; set; }
public string SourceData { get; set; }
}
And it's inside our SomeDbContext like so:
public class SomeDbContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<SomeTable> SomeTables { get; set; }
}
This table in Db has SourceData field as varchar(16) like so:
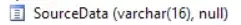
Now we'll try to insert value that is longer than 16 characters into this field and capture this information:
public void SaveSomeTableEntity()
{
var connectionString = "server=SERVER_NAME;database=DB_NAME;User ID=SOME_ID;Password=SOME_PASSWORD;Connection Timeout=200";
using (var context = new SomeDbContext(connectionString))
{
var someTableEntity = new SomeTable()
{
SourceData = "Blah-Blah-Blah-Blah-Blah-Blah"
};
context.SomeTables.Add(someTableEntity);
try
{
context.SaveChanges();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
if (ex.GetBaseException().Message == "String or binary data would be truncated.\r\nThe statement has been terminated.")
{
var badFieldsReport = "";
List<string> badFields = new List<string>();
// YOU GOT YOUR FIELDS RIGHT HERE:
var longFields = FindLongBinaryOrStringFields(someTableEntity, connectionString);
foreach (var longField in longFields)
{
badFields.Add(longField.Key);
badFieldsReport += longField.Value + "\n";
}
}
else
throw;
}
}
}
The badFieldsReport will have this value:
'SourceData' column cannot take the value of
'Blah-Blah-Blah-Blah-Blah-Blah' because the max length it can take is
16.