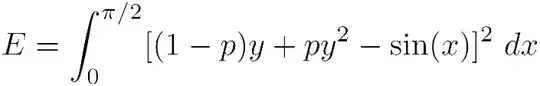Aug, 2022 Update:
You can remove "SAVE" button, "Save and continue editing" button, "Save and add another" button and "Delete" button from a specific admin.
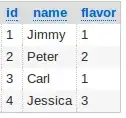
For example, this is "Person" model in "store" app below:
# "store/models.py"
from django.db import models
class Person(models.Model):
first_name = models.CharField(max_length=30)
last_name = models.CharField(max_length=30)
def __str__(self):
return self.first_name + " " + self.last_name
class Meta:
verbose_name = "Person"
verbose_name_plural = "Person"
Then, this is "Person" admin in "store" app below:
# "store/admin.py"
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Person
@admin.register(Person)
class PersonAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
pass
Then, this is how "Add person" page looks like:
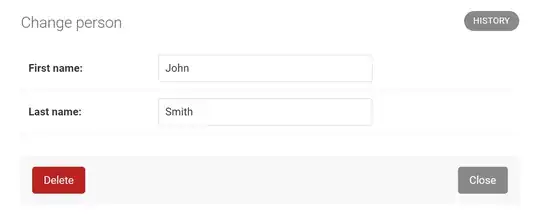
Then, this is how "Change person" page looks like:
Then, this is how "Select person to change" page looks like:

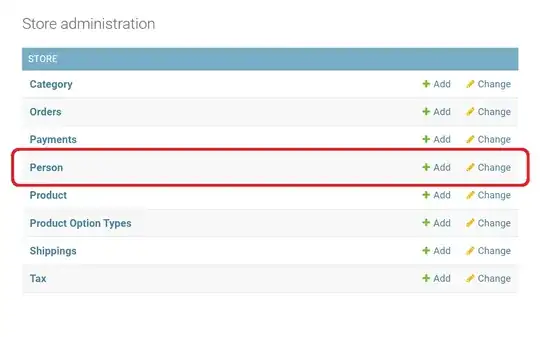
Then, this is how "Person" admin on "Store administration" page looks like:
First, to remove "SAVE" button, set "False" to "extra_context['show_save']" in "changeform_view()" as shown below:
# "store/admin.py"
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Person
@admin.register(Person)
class PersonAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
def changeform_view(self, request, object_id=None, form_url='', extra_context=None):
extra_context = extra_context or {}
extra_context['show_save'] = False # Here
return super().changeform_view(request, object_id, form_url, extra_context)
Then, "SAVE" button is removed from "Add person" page and "Change person" page. *Actually, "SAVE" button is replaced with "Close" buttom as shown below:
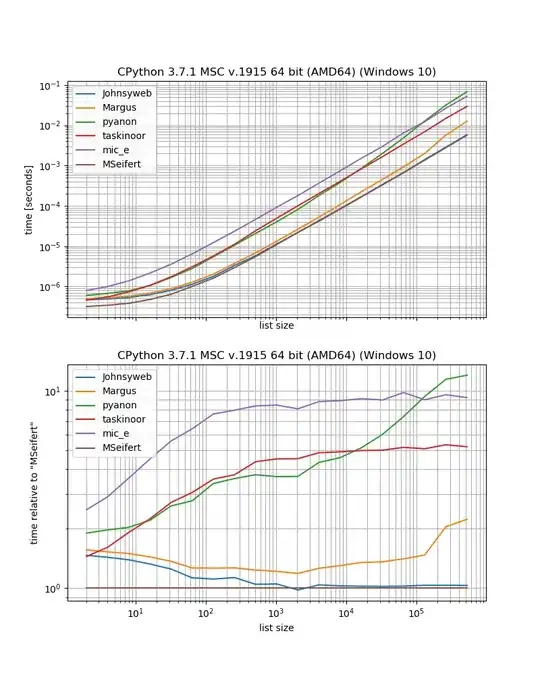

Next, to remove "Save and continue editing" button, set "False" to "extra_context['show_save_and_continue']" in "changeform_view()" as shown below:
# "store/admin.py"
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Person
@admin.register(Person)
class PersonAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
def changeform_view(self, request, object_id=None, form_url='', extra_context=None):
extra_context = extra_context or {}
extra_context['show_save'] = False
extra_context['show_save_and_continue'] = False # Here
return super().changeform_view(request, object_id, form_url, extra_context)
Then, "Save and continue editing" button is removed from "Add person" page and "Change person" page as shown below:
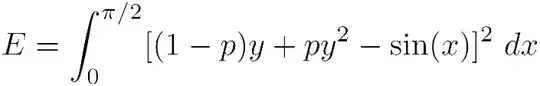
Next, to remove "Save and add another" button, return "False" in "has_add_permission()" as shown below. *After this, "Add person" page can no longer be accessed:
# "store/admin.py"
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Person
@admin.register(Person)
class PersonAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
def changeform_view(self, request, object_id=None, form_url='', extra_context=None):
extra_context = extra_context or {}
extra_context['show_save'] = False
extra_context['show_save_and_continue'] = False
return super().changeform_view(request, object_id, form_url, extra_context)
def has_add_permission(self, request, obj=None): # Here
return False
Then, "Save and add another" button is removed from "Change person" page as shown below:
Then, "ADD PERSON" button is also removed from "Select person to change" page as shown below:
Then, "➕ADD" button is also removed from "Person" admin on "Store administration" page as shown below:
Next, to remove "Delete" button, set "False" to "extra_context['show_delete']" in "changeform_view()" as shown below:
# "store/admin.py"
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Person
@admin.register(Person)
class PersonAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
def changeform_view(self, request, object_id=None, form_url='', extra_context=None):
extra_context = extra_context or {}
extra_context['show_save'] = False
extra_context['show_save_and_continue'] = False
extra_context['show_delete'] = False # Here
return super().changeform_view(request, object_id, form_url, extra_context)
def has_add_permission(self, request, obj=None):
return False
Then, "Delete" button is removed from "Change person" page as shown below:
Actually, you can also remove "Delete" button by returning "False" in "has_delete_permission()" as shown below:
# "store/admin.py"
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Person
@admin.register(Person)
class PersonAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
def changeform_view(self, request, object_id=None, form_url='', extra_context=None):
extra_context = extra_context or {}
extra_context['show_save'] = False
extra_context['show_save_and_continue'] = False
# extra_context['show_delete'] = False
return super().changeform_view(request, object_id, form_url, extra_context)
def has_add_permission(self, request, obj=None):
return False
def has_delete_permission(self, request, obj=None): # Here
return False
Then, "Delete" button is removed from "Change person" page as shown below:

Then, "Action" select dropdown box is also removed from "Select person to change" page as shown below:
In addition, you can make the fields on "Change person" page unchangeable by returning "False" in "has_change_permission()" as shown below:
# "store/admin.py"
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Person
@admin.register(Person)
class PersonAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
def changeform_view(self, request, object_id=None, form_url='', extra_context=None):
extra_context = extra_context or {}
extra_context['show_save'] = False
extra_context['show_save_and_continue'] = False
# extra_context['show_delete'] = False
return super().changeform_view(request, object_id, form_url, extra_context)
def has_add_permission(self, request, obj=None):
return False
def has_delete_permission(self, request, obj=None):
return False
def has_change_permission(self, request, obj=None): # Here
return False
Then, the fields on "Change person" page are made unchangeable as shown below:
Then, "✏️Change" button is replaced with "️View" for "Person" admin on "Store administration" page as shown below:
In addition, you can remove "Person" admin from "Store administration" page by returning "False" in "has_view_permission()" as shown below:
# "store/admin.py"
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Person
@admin.register(Person)
class PersonAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
def changeform_view(self, request, object_id=None, form_url='', extra_context=None):
extra_context = extra_context or {}
extra_context['show_save'] = False
extra_context['show_save_and_continue'] = False
# extra_context['show_delete'] = False
return super().changeform_view(request, object_id, form_url, extra_context)
def has_add_permission(self, request, obj=None):
return False
def has_delete_permission(self, request, obj=None):
return False
def has_change_permission(self, request, obj=None):
return False
def has_view_permission(self, request, obj=None): # Here
return False
Then, "Person" admin is removed from "Store administration" page as shown below:
Finally, you can replace "changeform_view()" with "render_change_form()" which can also remove "SAVE" button, "Save and continue editing" button and "Delete" button with "context.update()" as shown below:
# "store/admin.py"
from django.contrib import admin
from .models import Person
@admin.register(Person)
class PersonAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
# Here
def render_change_form(self, request, context, add=False, change=False, form_url='', obj=None):
context.update({
'show_save': False, # Here
'show_save_and_continue': False, # Here
# 'show_delete': False, # Here
})
return super().render_change_form(request, context, add, change, form_url, obj)
def has_add_permission(self, request, obj=None):
return False
def has_delete_permission(self, request, obj=None):
return False
def has_change_permission(self, request, obj=None):
return False
def has_view_permission(self, request, obj=None):
return False