where do i start on writing plugin test? I have written some toy plugins and would like to start on doing TDD with my plugins.
-
What kind of functionality would you like to test? As a matter of fact, JUnit plugin tests are just plain JUnit tests, there is nothing Eclipse-specific about them. The only difference is, that if you run you JUnit test as a JUnit plugin test, they will run inside an instance of Eclipse. – Zsolt Török Jun 03 '09 at 15:45
-
from the plugin test, how do you interact with eclipse? for example programmatically post a event to do some actions? – zeroin23 Jun 05 '09 at 13:00
1 Answers
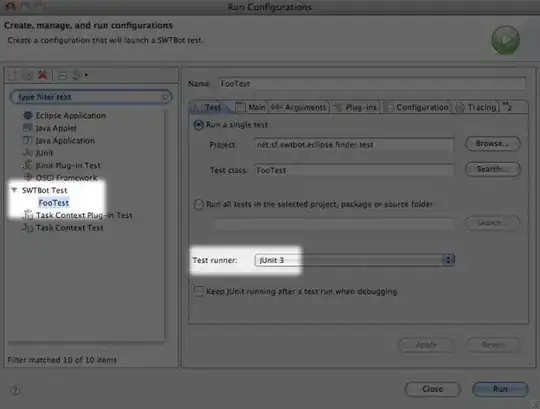
If your plugin are RCP (Rich Client Platform) plugins, with SWT, you could use SWTBot.
Those test can be encapsulated into JUnit one:
If your plugins are OSGi-based, you must be aware that OSGi bundle runs it's own class loader and therefore the classes appear not to be in the same package.
See "Is OSGi the enemy of JUnit tests?"
Make your test plugin a fragment.
One problem is that other plugins cannot access classes defined in fragments (as Patrick Paulin points out in a more detailed discussion about fragments in unit tests).
Another problem is thatplugin.xmlin a fragment is ignored. And therefore you test plugin cannot contribute
From Patrick's article:
A fragments looks much like a plug-in from the outside. It is represented as a separate project in your workspace, it contains a manifest that describes its contents, it is built and deployed as a jar. What makes a fragment different is that it contributes it’s resources at runtime to a single host plug-in. The classes in the fragment are therefore loaded by the host plug-in’s classloader.
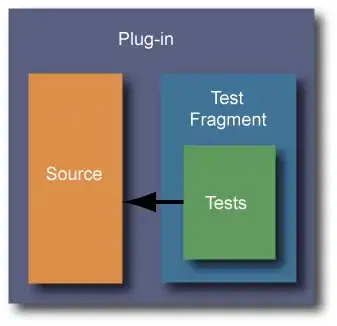
By placing our unit tests in fragments, we can provide our tests access to the non-public methods of the classes under test. Also, because the source code and test code are actually part of the same plug-in, there are no issues related to non-exported packages. Test classes will have access to all packages in the plug-in, whether they are exported or not.
The main disadvantage to this fragment based approach is that it is difficult to aggregate unit tests into a master test suite. While it’s easy to create a test suite that includes the tests within a fragment, it’s not so easy to create a suite that includes the tests in multiple fragments.
If your plugins need just some simple testing, a JUnit test suite is enough
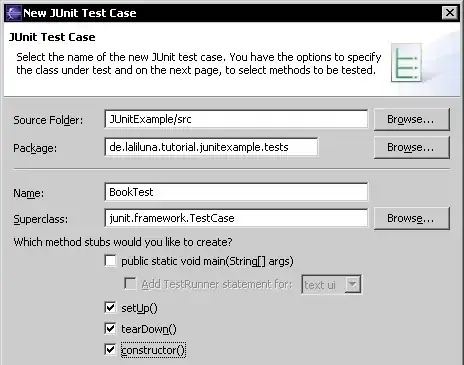
Create a new test case BookTest in the package test.yourpackage, Right click on the package and choose "
New > JUnit Test Case".