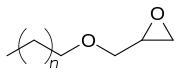
 n = 10-11 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| EC Number |
|
| |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
C12-C13 alcohol glycidyl ether is a mixture of organic chemicals in the glycidyl ether family.[1] It is a mixture of mainly 12 and 13 carbon chain alcohols, also called fatty alcohols that have been glycidated.[2] It is an industrial chemical used as a surfactant but primarily for epoxy resin viscosity reduction.[3][4] It has the CAS number 120547-52-6.[5]
Manufacture
A fatty alcohol mixture rich in C12-C13 alcohols is placed in a reactor with a Lewis acid catalyst. Epichlorohydrin is then added slowly to control the exotherm. The reaction results in the formation of the halohydrins.[6] This is followed by a caustic dehydrochlorination, to form C12-C13 alcohol glycidyl ether.[7] The waste products are water and sodium chloride and excess caustic soda.[8] One of the quality control tests would involve measuring the Epoxy value by determination of the epoxy equivalent weight.
Synonyms
The material has a number of synonyms.[9]
- Oxirane, mono (C12-13-alkyloxy) methyl derivatives
- Alkyl(C12-C13) glycidyl ether
- Alkyl glycidyl ether
- Oxirane, Mono (C12-C13 alkoxymethyl) methyl derivatives
- (C12-C13)alkylglycidyl ether
- Oxirane, 2-[(C12-13-alkyloxy)methyl] derivatives
Uses
As an epoxy modifier it is classed as an epoxy reactive diluent.[10] It is one of a family of glycidyl ethers available used for viscosity reduction of epoxy resins.[11][12] These are then further formulated into coatings, sealants, adhesives, and elastomers.[13][14] Resins with this diluent tend to show improved workability.[15] It is also used to synthesize other molecules.[16][17] The use of the diluent does effect mechanical properties and microstructure of epoxy resins.[18][19]
Toxicology
The toxicology is fairly well known, and it is classed as a skin irritant.[20]
See also
References
- ↑ Chambers, Michael. "ChemIDplus - 120547-52-6 - Oxirane, 2-((C12-13-alkyloxy)methyl) derivs. - Searchable synonyms, formulas, resource links, and other chemical information". chem.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 2022-04-29. Retrieved 2022-04-29.
- ↑ "120547-52-6 CAS MSDS (Oxirane, mono(C12-13-alkyloxy)methyl derivs.) Melting Point Boiling Point Density CAS Chemical Properties". www.chemicalbook.com. Archived from the original on 2022-04-29. Retrieved 2022-04-29.
- ↑ Jagtap, Ameya Rajendra; More, Aarti (2022-08-01). "Developments in reactive diluents: a review". Polymer Bulletin. 79 (8): 5667–5708. doi:10.1007/s00289-021-03808-5. ISSN 1436-2449. S2CID 235678040.
- ↑ Verkoyen, Patrick; Frey, Holger (August 2020). "Long‐Chain Alkyl Epoxides and Glycidyl Ethers: An Underrated Class of Monomers". Macromolecular Rapid Communications. 41 (15): 2000225. doi:10.1002/marc.202000225. ISSN 1022-1336. PMID 32567153. S2CID 219973760.
- ↑ "Alkyl (C12-C13) glycidyl ether - Hazardous Agents | Haz-Map". haz-map.com. Archived from the original on 2022-05-12. Retrieved 2022-04-29.
- ↑ "Process for the preparation of glycidyl ethers- US Patent 5162547" (PDF). November 1992.
- ↑ SJÖVOLD, HENRICK (2015). "Solvent-Free Synthesis of Glycidyl Ethers : Investigating Factors Influencing the Yield of Alkyl Glycidyl Ethers Master of Science Thesis" (PDF). Chalmers University Sweden. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2017-08-15. Retrieved 2022-05-12.
- ↑ "Preparation method of alkyl glycidyl ether - Patent CN-113429367-A - PubChem". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 2022-04-12. Retrieved 2022-04-12.
- ↑ "120547-52-6 CAS MSDS (Oxirane, mono(C12-13-alkyloxy)methyl derivs.) Melting Point Boiling Point Density CAS Chemical Properties". www.chemicalbook.com. Archived from the original on 2022-04-29. Retrieved 2022-04-29.
- ↑ Monte, Salvatore J. (1998), Pritchard, Geoffrey (ed.), "Diluents and viscosity modifiers for epoxy resins", Plastics Additives: An A-Z reference, Polymer Science and Technology Series, Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, vol. 1, pp. 211–216, doi:10.1007/978-94-011-5862-6_24, ISBN 978-94-011-5862-6, archived from the original on 2022-04-11, retrieved 2022-03-29
- ↑ Office, European Patent. "European publication server". data.epo.org. Archived from the original on 2022-05-12. Retrieved 2022-04-29.
- ↑ Ali, M.; Hammami, A. (July 2005). "Experimental modeling of the cure behavior of a formulated blend of DGEBA epoxy and C12-C14 glycidyl ether as a reactive diluent". Polymer Composites. 26 (5): 593–603. doi:10.1002/pc.20131. ISSN 0272-8397. Archived from the original on 2022-04-12. Retrieved 2022-05-12.
- ↑ Howarth G.A "Synthesis of a legislation compliant corrosion protection coating system based on urethane, oxazolidine and waterborne epoxy technology" pages 23,24,39 Master of Science Thesis April 1997 Imperial College London
- ↑ Monte, Salvatore J. (1998), Pritchard, Geoffrey (ed.), "Diluents and viscosity modifiers for epoxy resins", Plastics Additives: An A-Z reference, Polymer Science and Technology Series, Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, vol. 1, pp. 211–216, doi:10.1007/978-94-011-5862-6_24, ISBN 978-94-011-5862-6, archived from the original on 2022-04-11, retrieved 2022-04-12
- ↑ Ozeren Ozgul, Eren; Ozkul, M. Hulusi (2018-01-15). "Effects of epoxy, hardener, and diluent types on the workability of epoxy mixtures". Construction and Building Materials. 158: 369–377. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.10.008. ISSN 0950-0618. Archived from the original on 2022-05-12. Retrieved 2022-05-12.
- ↑ Urata, Kouichi; Takaishi, Naotake (September 1994). "The alkyl glycidyl ether as synthetic building blocks". Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society. 71 (9): 1027–1033. doi:10.1007/BF02542274. S2CID 96776835.
- ↑ Verkoyen, Patrick; Frey, Holger (August 2020). "Long‐Chain Alkyl Epoxides and Glycidyl Ethers: An Underrated Class of Monomers". Macromolecular Rapid Communications. 41 (15): 2000225. doi:10.1002/marc.202000225. ISSN 1022-1336. PMID 32567153.
- ↑ Khalina, Morteza; Beheshty, Mohammad Hosain; Salimi, Ali (2019-08-01). "The effect of reactive diluent on mechanical properties and microstructure of epoxy resins". Polymer Bulletin. 76 (8): 3905–3927. doi:10.1007/s00289-018-2577-6. ISSN 1436-2449. S2CID 105389177.
- ↑ Pastarnokienė, Liepa; Jonikaitė-Švėgždienė, Jūratė; Lapinskaitė, Neringa; Kulbokaitė, Rūta; Bočkuvienė, Alma; Kochanė, Tatjana; Makuška, Ričardas (2023-07-01). "The effect of reactive diluents on curing of epoxy resins and properties of the cured epoxy coatings". Journal of Coatings Technology and Research. 20 (4): 1207–1221. doi:10.1007/s11998-022-00737-4. ISSN 1935-3804. S2CID 256749849.
- ↑ Canada, Environment and Climate Change (2020-08-07). "Screening assessment - Epoxides and Glycidyl Ethers Group". www.canada.ca. Archived from the original on 2022-03-24. Retrieved 2022-04-29.
Further reading
- Epoxy resin technology. Paul F. Bruins, Polytechnic Institute of Brooklyn. New York: Interscience Publishers. 1968. ISBN 0-470-11390-1. OCLC 182890.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - Flick, Ernest W. (1993). Epoxy resins, curing agents, compounds, and modifiers : an industrial guide. Park Ridge, NJ. ISBN 978-0-8155-1708-5. OCLC 915134542.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Lee, Henry (1967). Handbook of epoxy resins. Kris Neville ([2nd, expanded work] ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. ISBN 0-07-036997-6. OCLC 311631322.
- "Dow Epoxy Resins" (PDF).