Tested on Windows (04/22/2021). Easy (no installations required).
1. Project configuration
In your project root run in Powershell (or CMD):
npx mkcert create-ca
npx mkcert create-cert
Your webpack.config.js:
devServer: {
// ...
https: {
key: fs.readFileSync("cert.key"),
cert: fs.readFileSync("cert.crt"),
ca: fs.readFileSync("ca.crt"),
},
// ....
},
2. Install certificate
Double-click on ca.crt > Install Certificate > ...
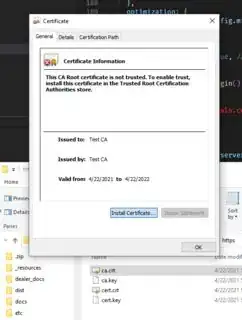
... > Current User > Place all certificates in the following store > Trusted Root Certification Authorities > ...
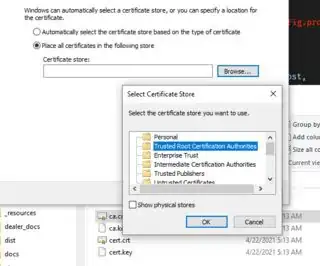
... > Finish > Yes
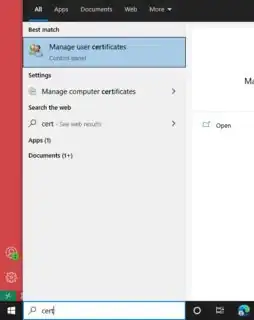
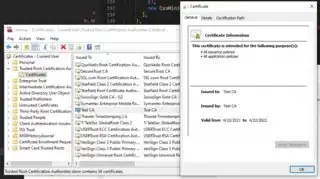
3. Check correct installation
Start > Type: "cert" > Manage User Certificates > ...
... > Trusted Root Certification Authorities > Certificates > Test CA
4. Reload & Test
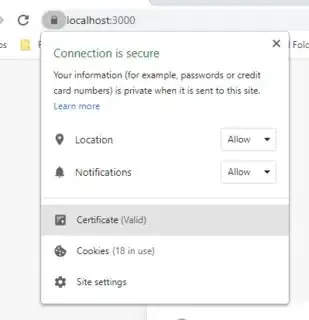
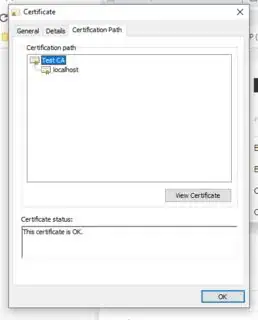
Reload your browser, Start yout webpack dev server and check the SSL Certificate validity:
Additional steps
If you get this error:
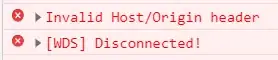
You can add this configuration to your webpack.config.js:
devServer: {
// ...
// https: { ... }
disableHostCheck: true,
// ....
},
For more info:
https://webpack.js.org/configuration/dev-server/#devserverhttps
https://www.npmjs.com/package/mkcert







