I using Visual Studio 2010 (.NET 4). I need to create a COM object (in C#) and have no idea how to get started (what type of project to use,etc.)
Asked
Active
Viewed 9.3k times
48
-
Doesn't have to be an ActiveX if anyone know how to create a COM in C# that should get me started – Eyal Jul 29 '10 at 07:12
-
@Bujutsu however, the ActiveX part will be the more difficult to find information on: simple WinForms is widely demonstrated. – Richard Nov 24 '15 at 13:34
-
@Richard the peculiar thing about my Answer is that I have given explicit and comprehensive full solution for a windows form secure activex. Another not so easy difference is the different IDE of the linked answer, wich is for Visual Studio 2010. Thank you for your comment. – Giulio Caccin Nov 24 '15 at 16:13
-
Well, if anyone need a help yet, this link is a very good start: https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/asiatech/2011/12/05/how-to-develop-and-deploy-activex-control-in-c/ – Andersson Melo Jun 29 '18 at 00:57
3 Answers
70
OK I found the solution and I'll write it here for the common good.
- Start VS2010 as administrator.
- Open a class library project (exmaple - MyProject).
- Add a new interface to the project (see example below).
- Add a
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;to the file - Add the attributes InterfaceType, Guid to the interface.
- You can generate a Guid using Tools->Generate GUID (option 4).
- Add a class that implement the interface.
- Add the attributes ClassInterface, Guid, ProgId to the interface.
ProgId convention is {namespace}.{class} - Under the Properties folder in the project in the AssemblyInfo file set ComVisible to true.
- In the project properties menu, in the build tab mark "Register for COM interop"
- Build the project
now you can use your COM object by using it's ProgID.
example: the C# code:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace Launcher
{
[InterfaceType(ComInterfaceType.InterfaceIsDual), Guid("XXXXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXXXXXXXXXX")]
public interface ILauncher
{
void launch();
}
[ClassInterface(ClassInterfaceType.None), Guid("YYYYYYYY-YYYY-YYYY-YYYY-YYYYYYYYYYY"), ProgId("Launcher.Launcher")]
public class Launcher : ILauncher
{
private string path = null;
public void launch()
{
Console.WriteLine("I launch scripts for a living.");
}
}
}
and VBScript using the COM:
set obj = createObject("PSLauncher.PSLauncher")
obj.launch()
and the output will be:
I launch scripts for a living
Stephen Ostermiller
- 23,933
- 14
- 88
- 109
Eyal
- 1,191
- 1
- 9
- 7
-
2Additionally, if you built the assembly and are having trouble using it: ("Could not create object" error) http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1208180/classic-asp-using-com-on-x64-windows-server-2008-and-iis7 http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1281052/classic-asp-using-com-net-interop-64-bit-windows-server-2008-iis-7-server-crea/1343271#1343271 – Zachary Yates Dec 05 '12 at 22:47
-
i followed the above steps and my macro is as follows Sub test() Dim ob As Object Set ob = CreateObject("ClassCom.Name") Dim name As String name = ob.launc() End Sub It said "Error 429" activex cant create object what might have gone wrong? – Vignesh Subramanian May 05 '15 at 05:07
-
I followed the same but no luck. getting same error Activex cant created when i launch the exe in remote machine using VB.Net – Arul Sidthan Jul 16 '18 at 07:13
-
Sample VB.Net code: Protected Sub Unnamed1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Dim strRemoteServer = "xxxxx" Dim strUser = "xxx" Dim strPassword = "yyy" Dim strCommand strCommand = "" Dim objWMIService = GetObject("winmgmts:" & "{impersonationlevel=impersonate}!\\" & strRemoteServer & "\root\cimv2") Dim objProcess = objWMIService.Get("Win32_Process") Dim objQWCreate = objProcess.Create(strCommand) End Sub Error : 'Cannot create ActiveX component.' – Arul Sidthan Jul 16 '18 at 07:36
16
Creation Steps
- Start Visual Studio 2013 as administrator
- Install Visual Studio extension Microsoft Visual Studio Installer Projects
- Create a class library project (WinFormActivex)
- Create your example window form (MainWindow)
- Create a new component interface(ILauncher)
- Create a new security interface (IObjectSafety)
- Create the component control (Launcher) that implement interfaces and launch the window.
- Check that all GUIDs are generated by you
- Check that the project is marked for COM
- Create the setup project (LauncherInstaller) with the primary output of WinFormActivex with the property
Register = vsdrpCOM - Install LauncherInstaller
- Run your test page in explorer (test.html)
MainWindow You can create a normal Form, here is pre-generated.
public partial class MainWindow : Form
{
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
/// <summary>
/// Required designer variable.
/// </summary>
private System.ComponentModel.IContainer components = null;
/// <summary>
/// Clean up any resources being used.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="disposing">true if managed resources should be disposed; otherwise, false.</param>
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
if (disposing && (components != null))
{
components.Dispose();
}
base.Dispose(disposing);
}
#region Windows Form Designer generated code
/// <summary>
/// Required method for Designer support - do not modify
/// the contents of this method with the code editor.
/// </summary>
private void InitializeComponent()
{
this.textBox1 = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox();
this.textBox2 = new System.Windows.Forms.TextBox();
this.SuspendLayout();
//
// textBox1
//
this.textBox1.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(42, 23);
this.textBox1.Name = "textBox1";
this.textBox1.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(100, 20);
this.textBox1.TabIndex = 0;
//
// textBox2
//
this.textBox2.Location = new System.Drawing.Point(42, 65);
this.textBox2.Name = "textBox2";
this.textBox2.Size = new System.Drawing.Size(100, 20);
this.textBox2.TabIndex = 0;
//
// MainWindow
//
this.AutoScaleDimensions = new System.Drawing.SizeF(6F, 13F);
this.AutoScaleMode = System.Windows.Forms.AutoScaleMode.Font;
this.ClientSize = new System.Drawing.Size(284, 261);
this.Controls.Add(this.textBox2);
this.Controls.Add(this.textBox1);
this.Name = "MainWindow";
this.Text = "MainWindow";
this.ResumeLayout(false);
this.PerformLayout();
}
#endregion
private System.Windows.Forms.TextBox textBox1;
private System.Windows.Forms.TextBox textBox2;
}
ILauncher
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace WinFormActivex
{
[ComVisible(true)]
[InterfaceType(ComInterfaceType.InterfaceIsDual)]
[Guid("94D26775-05E0-4B9C-BC73-C06FE915CF89")]
public interface ILauncher
{
void ShowWindow();
}
}
IObjectSafety
[ComImport()]
[Guid("51105418-2E5C-4667-BFD6-50C71C5FD15C")]
[InterfaceType(ComInterfaceType.InterfaceIsIUnknown)]
interface IObjectSafety
{
[PreserveSig()]
int GetInterfaceSafetyOptions(ref Guid riid, out int pdwSupportedOptions, out int pdwEnabledOptions);
[PreserveSig()]
int SetInterfaceSafetyOptions(ref Guid riid, int dwOptionSetMask, int dwEnabledOptions);
}
Launcher Please generate your GUID here.
[ComVisible(true)]
[ClassInterface(ClassInterfaceType.None)]
[Guid("D100C392-030A-411C-92B6-4DBE9AC7AA5A")]
[ProgId("WinFormActivex.Launcher")]
[ComDefaultInterface(typeof(ILauncher))]
public class Launcher : UserControl, ILauncher, IObjectSafety
{
#region [ ILauncher ]
public void ShowWindow()
{
var f = new MainWindow();
f.StartPosition = FormStartPosition.Manual;
f.Location = Screen.AllScreens[0].Bounds.Location;
f.WindowState = FormWindowState.Normal;
f.WindowState = FormWindowState.Maximized;
f.ShowInTaskbar = false;
f.Show();
}
#endregion
#region [ IObjectSafety ]
public enum ObjectSafetyOptions
{
INTERFACESAFE_FOR_UNTRUSTED_CALLER = 0x00000001,
INTERFACESAFE_FOR_UNTRUSTED_DATA = 0x00000002,
INTERFACE_USES_DISPEX = 0x00000004,
INTERFACE_USES_SECURITY_MANAGER = 0x00000008
};
public int GetInterfaceSafetyOptions(ref Guid riid, out int pdwSupportedOptions, out int pdwEnabledOptions)
{
ObjectSafetyOptions m_options = ObjectSafetyOptions.INTERFACESAFE_FOR_UNTRUSTED_CALLER | ObjectSafetyOptions.INTERFACESAFE_FOR_UNTRUSTED_DATA;
pdwSupportedOptions = (int)m_options;
pdwEnabledOptions = (int)m_options;
return 0;
}
public int SetInterfaceSafetyOptions(ref Guid riid, int dwOptionSetMask, int dwEnabledOptions)
{
return 0;
}
#endregion
}
test.html Please check that your CLSID match (Launcher) GUID.
<html>
<head>
<objectname="activexLauncher" style='display:none' id='activexLauncher' classid='CLSID:D100C392-030A-411C-92B6-4DBE9AC7AA5A' codebase='WinFormActivex'></object>
<script language="javascript">
<!-- Load the ActiveX object -->
var x = new ActiveXObject("WinFormActivex.Launcher");
alert(x.GetText());
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
References
Community
- 1
- 1
Giulio Caccin
- 2,962
- 6
- 36
- 57
13
You could use a class library project. Declare a type with methods that will be exposed as a COM object.
Make sure that the assembly has been made COM-visible:
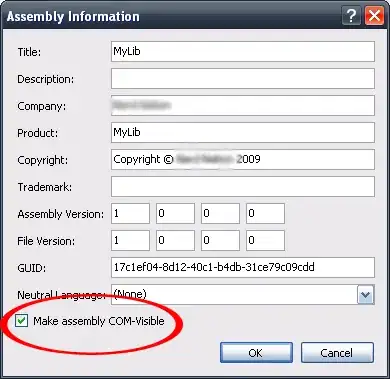
And finally register it using regasm.exe:
regasm.exe /codebase mylib.dll
Now the assembly is exposed as a COM object and the type you declared can be consumed by any client that supports COM.
Community
- 1
- 1
Darin Dimitrov
- 1,023,142
- 271
- 3,287
- 2,928
-
1"Declare a type with methods that will be exposed as a COM object" ? Do i have to explicity implement an interface and give it a GUID or does the "Make Assem. COM Visible" option all that? – CloudyMarble Jun 08 '12 at 06:14
-
I also do not understand this. What did you mean by "Declare a type with methods that will be exposed as a COM object" ? – PeakGen May 14 '13 at 10:20