What's happening here is that git thinks the local repository's history isn't the same as the the remote repository's history. If you dig into how git actually works, it's pretty unlikely that it's wrong, so my guess would be that you've made a change on the remote repository since you ran that last git pull command.
This quote confirms this:
EDIT: Thank you guys, I did delete a file from the remote repo after the pull. I did a pull again, made the changes again and pushed without a problem.
Since you now know what the cause was, you realize that you can avoid it by only making local changes when you know the remote hasn't been changed, but that doesn't sound like a very good workflow, especially if multiple people are working on a repository. Besides, one of the strengths of git is supposed to be that multiple people can work on the same repository at the same time and all push to the same remote repository.
Let's look at what commands you have available to you that can be used to deal with this better in the future:
fetch
You can always safely fetch the changes from the remote repository without affecting your working copy or local branches. This will download the new history from the remote repository into what's known as a 'tracking branch', but it doesn't apply it to any of your local branches, and it doesn't touch your 'working copy'.
merge
A merge will try to apply the changes in another branch to the head of the branch you're on. It can be used between local branches, or to merge changes from tracking branches into a local branch. However it does so using a 'merge commit', allowing for non-linear history. Git has no issue with this, and in small doses humans aren't usually too bothered by it either:
The more you do it though, the more complex the history becomes, and mere humans can have some difficulty keeping track of things as the complexity increases:
pull
This is really just a fetch followed by a merge:

rebase
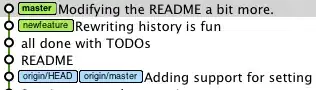
This is a form of rewriting history. Basically you're merging the changes from one branch into another, however unlike a regular merge, you don't just tie the two branches together and call it good, instead you take off the changes you've made on one branch after the two branches split, apply the changes from the other branch, then reapply the changes that you took off, leaving a nice, linear history.
Before:

After:
pull --rebase
This (like a regular pull) uses fetch to get the remote changes, but instead of following up with a merge, it does a rebase, so you can have the ease of using only having to run one command and also have a nice, linear history when you look back on what you've done.
[All images in this answer are also a link to where I got them from.]




