AFAIK, there is no way to hide the paths, because the VS Code Integrated Terminal is basically using your OS/system's underlying terminal. And running Python scripts on a terminal requires the following form:
<path/to/python/interpreter> <path/to/python/file>
If you want a "cleaner" console output, you could create a debug/launch configuration for Python, then set the console configuration to internalConsole:
.vscode/launch.json
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "run-my-script",
"type": "python",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/path/to/your_script.py",
"console": "internalConsole"
}
]
}
That would display the output in the Debug Console tab rather than the Terminal tab. There will be no more paths, just whatever your script prints out to the console.
sample output:
Unfortunately, if your Python code uses and requires manual input() from the user, using the Debug Console and the internalConsole solution would not work. It will show this error:
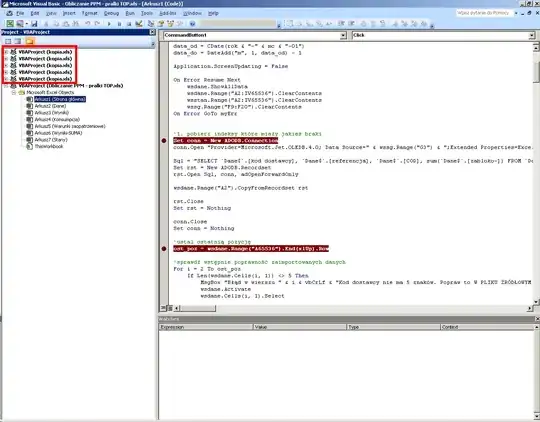
There is no direct solution to that, to having a "clean" output and allowing manual user input(). You might want to consider instead reading your program inputs from a file or passing them as command line arguments. VS Code supports passing in arguments ([args]) when running your script
<path/to/python/interpreter> <path/to/python/file> [args]
using the "args" option in the launch.json file. Here is a simple example with sys.argv:
python code
import sys
# This is always path to the script
arg_0 = sys.argv[0]
# Same sequence as "args" in launch.json
arg_1 = sys.argv[1]
arg_2 = sys.argv[2]
print(arg_1)
print(arg_2)
.vscode/launch.json
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "run-my-script",
"type": "python",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/path/to/your_script.py",
"console": "internalConsole",
"args": [
"89",
"abc"
]
}
]
}
sample output