as I mentioned in the comments you got 2 options either use OpenGL rendering or compute entirely on CPU side without it. Let start with rendering first:
render your scene
but instead of color of torus and stuff use integer indexes (for example 0 empty space, 1 obstacle, 2 torus ...) you can even have separate indexes for each object in the world so you know exactly which one is hit etc ...
so: clear screen with empty color, render your scene (using indexes instead of color with glColor??(???)) without lighting or shading or whatever. But Do not swap buffers !!! as that would show the stuff on screen and cause flickering.
read rendered screen and depth buffers
you simply use glReadPixels to copy your screen and depth buffers into CPU side memory (1D arrays) lets call them scr[],zed[].
scan the scr[] for color matching torus indexes
simply loop through all pixels and if torus pixel found check its depth. If it is close enough to camera you found your collision.
render normally
now clear screen again and render your screen with colors and lighting... now you can swap buffers too.
Beware depth buffer will be non linear which requires linearization to obtain original depth in world units. For more about it and example of reading both scr,zed see:
The other approach is is much faster in case you have not too many torus'es. You simply compute intersection between camera znear plane and torus. Which boils down to either AABB vs rectangle intersection or cylinder vs. rectangle intersection.
However if you not familiar with 3D vector math you might get lost quickly.
let assume the torus is described by AABB. Then intersection between that and rectangle boils down to checking intersection between line (each edge of AABB) and rectangle. So simply finding instersection between plane and line and checking if the point is inside rectangle.
if our rectangle is defined by its vertexes in CW or CCW order (p0,p1,p2,p3) and line by endpoints q0,q1 then:
n = normalize(cross(p1-p0,p2-p1)) // is rectangle normal
dq = normalize(q1-q0) // is line direction
q = q0 + dq*dot(dq,p1-p0) // is plane/line intersection
So now just check if q is inside rectangle. There are 2 ways either test if all crosses between q-edge_start and edge_end-edge_start have the same direction or all dots between all edge_normal and q-edge_point has the same sign or zero.
The problem is that both AABB and rectangle must be in the same coordinate system so either transform AABB into camera coordinates by using modelview matrix or transform the rectangle into world coordinates using inverse of modelview. The latter is better as you do it just once instead of transforming each torus'es AABB ...
For more info about math side see:
The rectangle itself is just extracted from your camera matrix (part of modelviev) position, and x,y basis vectors gives you the "center" and axises of your rectangle... The size must be derived from the perspective matrix (or parameters you passed to it especially aspect ratio, FOV and znear)
Well first you need to obtain camera (view) matrix. The GL_MODELVIEW usually holds:
GL_MODELVIEW = Inverse(Camera)*Rendered_Object
so you need to find the place in your code where your GL_MODELVIEW holds just the Inverse(Camera) transformation and there place:
float aspect=float(xs)/float(ys); // aspect from OpenGL window resolution
float im[16],m[16],znear=0.1,zfar=100.0,fovx=60.0*M_PI/180.0;
vec3 p0,p1,p2,p3,o,u,v; // 3D vectors
// this is how my perspective is set
// glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
// glLoadIdentity();
// gluPerspective(fovx*180.0/(M_PI*aspect),aspect,znear,zfar);
// get camera matrix (must be in right place in code before model transformations)
glGetFloatv(GL_MODELVIEW_MATRIX,im); // get camera inverse matrix
matrix_inv(m,im); // m = inverse(im)
u =vec3(m[ 0],m[ 1],m[ 2]); // x axis
v =vec3(m[ 4],m[ 5],m[ 6]); // y axis
o =vec3(m[12],m[13],m[14]); // origin
o-=vec3(m[ 8],m[ 9],m[10])*znear; // z axis offset
// scale by FOV
u*=znear*tan(0.5*fovx);
v*=znear*tan(0.5*fovx/aspect);
// get rectangle coorners
p0=o-u-v;
p1=o+u-v;
p2=o+u+v;
p3=o-u+v;
// render it for debug
glColor3f(1.0,1.0,0.0);
glBegin(GL_QUADS);
glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0); glVertex3fv(p0.dat);
glColor3f(0.0,0.0,0.0); glVertex3fv(p1.dat);
glColor3f(0.0,0.0,1.0); glVertex3fv(p2.dat);
glColor3f(1.0,1.0,1.0); glVertex3fv(p3.dat);
glEnd();
Which basicaly loads the matrix into CPU side variables inverse it like this:
void matrix_inv(float *a,float *b) // a[16] = Inverse(b[16])
{
float x,y,z;
// transpose of rotation matrix
a[ 0]=b[ 0];
a[ 5]=b[ 5];
a[10]=b[10];
x=b[1]; a[1]=b[4]; a[4]=x;
x=b[2]; a[2]=b[8]; a[8]=x;
x=b[6]; a[6]=b[9]; a[9]=x;
// copy projection part
a[ 3]=b[ 3];
a[ 7]=b[ 7];
a[11]=b[11];
a[15]=b[15];
// convert origin: new_pos = - new_rotation_matrix * old_pos
x=(a[ 0]*b[12])+(a[ 4]*b[13])+(a[ 8]*b[14]);
y=(a[ 1]*b[12])+(a[ 5]*b[13])+(a[ 9]*b[14]);
z=(a[ 2]*b[12])+(a[ 6]*b[13])+(a[10]*b[14]);
a[12]=-x;
a[13]=-y;
a[14]=-z;
}
And compute the corners with perspective in mind as described above...
I used GLSL like vec3 but you can use any 3D math even own like float p0[3],.... You just need +,- and multiplying by constant.
Now the p0,p1,p2,p3 holds your znear camera screen corners in world coordinates.
[Edit1] example
I managed to put together simple example for this. Here support functiosn used first:
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void glutSolidTorus(float r,float R,int na,int nb) // render torus(r,R)
{
float *pnt=new float[(na+1)*(nb+1)*3*2]; if (pnt==NULL) return;
float *nor=pnt+((na+1)*(nb+1)*3);
float ca,sa,cb,sb,a,b,da,db,x,y,z,nx,ny,nz;
int ia,ib,i,j;
da=2.0*M_PI/float(na);
db=2.0*M_PI/float(nb);
glBegin(GL_LINES);
for (i=0,a=0.0,ia=0;ia<=na;ia++,a+=da){ ca=cos(a); sa=sin(a);
for ( b=0.0,ib=0;ib<=nb;ib++,b+=db){ cb=cos(b); sb=sin(b);
z=r*ca;
x=(R+z)*cb; nx=(x-(R*cb))/r;
y=(R+z)*sb; ny=(y-(R*sb))/r;
z=r*sa; nz=sa;
pnt[i]=x; nor[i]=nx; i++;
pnt[i]=y; nor[i]=ny; i++;
pnt[i]=z; nor[i]=nz; i++;
}}
glEnd();
for (ia=0;ia<na;ia++)
{
i=(ia+0)*(nb+1)*3;
j=(ia+1)*(nb+1)*3;
glBegin(GL_QUAD_STRIP);
for (ib=0;ib<=nb;ib++)
{
glNormal3fv(nor+i); glVertex3fv(pnt+i); i+=3;
glNormal3fv(nor+j); glVertex3fv(pnt+j); j+=3;
}
glEnd();
}
delete[] pnt;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
const int AABB_lin[]= // AABB lines
{
0,1,
1,2,
2,3,
3,0,
4,5,
5,6,
6,7,
7,4,
0,4,
1,5,
2,6,
3,7,
-1
};
const int AABB_fac[]= // AABB quads
{
3,2,1,0,
4,5,6,7,
0,1,5,4,
1,2,6,5,
2,3,7,6,
3,0,4,7,
-1
};
void AABBSolidTorus(vec3 *aabb,float r,float R) // aabb[8] = AABB of torus(r,R)
{
R+=r;
aabb[0]=vec3(-R,-R,-r);
aabb[1]=vec3(+R,-R,-r);
aabb[2]=vec3(+R,+R,-r);
aabb[3]=vec3(-R,+R,-r);
aabb[4]=vec3(-R,-R,+r);
aabb[5]=vec3(+R,-R,+r);
aabb[6]=vec3(+R,+R,+r);
aabb[7]=vec3(-R,+R,+r);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
void matrix_inv(float *a,float *b) // a[16] = Inverse(b[16])
{
float x,y,z;
// transpose of rotation matrix
a[ 0]=b[ 0];
a[ 5]=b[ 5];
a[10]=b[10];
x=b[1]; a[1]=b[4]; a[4]=x;
x=b[2]; a[2]=b[8]; a[8]=x;
x=b[6]; a[6]=b[9]; a[9]=x;
// copy projection part
a[ 3]=b[ 3];
a[ 7]=b[ 7];
a[11]=b[11];
a[15]=b[15];
// convert origin: new_pos = - new_rotation_matrix * old_pos
x=(a[ 0]*b[12])+(a[ 4]*b[13])+(a[ 8]*b[14]);
y=(a[ 1]*b[12])+(a[ 5]*b[13])+(a[ 9]*b[14]);
z=(a[ 2]*b[12])+(a[ 6]*b[13])+(a[10]*b[14]);
a[12]=-x;
a[13]=-y;
a[14]=-z;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
const int QUAD_lin[]= // quad lines
{
0,1,
1,2,
2,3,
3,0,
-1
};
const int QUAD_fac[]= // quad quads
{
0,1,2,3,
-1
};
void get_perspective_znear(vec3 *quad) // quad[4] = world coordinates of 4 corners of screen at znear distance from camera
{
vec3 o,u,v; // 3D vectors
float im[16],m[16],znear,zfar,aspect,fovx;
// get stuff from perspective
glGetFloatv(GL_PROJECTION_MATRIX,m); // get perspective projection matrix
zfar =0.5*m[14]*(1.0-((m[10]-1.0)/(m[10]+1.0)));// compute zfar from perspective matrix
znear=zfar*(m[10]+1.0)/(m[10]-1.0); // compute znear from perspective matrix
aspect=m[5]/m[0];
fovx=2.0*atan(1.0/m[5])*aspect;
// get stuff from camera matrix (must be in right place in code before model transformations)
glGetFloatv(GL_MODELVIEW_MATRIX,im); // get camera inverse matrix
matrix_inv(m,im); // m = inverse(im)
u =vec3(m[ 0],m[ 1],m[ 2]); // x axis
v =vec3(m[ 4],m[ 5],m[ 6]); // y axis
o =vec3(m[12],m[13],m[14]); // origin
o-=vec3(m[ 8],m[ 9],m[10])*znear; // z axis offset
// scale by FOV
u*=znear*tan(0.5*fovx);
v*=znear*tan(0.5*fovx/aspect);
// get rectangle coorners
quad[0]=o-u-v;
quad[1]=o+u-v;
quad[2]=o+u+v;
quad[3]=o-u+v;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
bool collideLineQuad(vec3 *lin,vec3 *quad) // return if lin[2] is colliding quad[4]
{
float t,l,u,v;
vec3 p,p0,p1,dp;
vec3 U,V,W;
// quad (rectangle) basis vectors
U=quad[1]-quad[0]; u=length(U); u*=u;
V=quad[3]-quad[0]; v=length(V); v*=v;
W=normalize(cross(U,V));
// convert line from world coordinates to quad local ones
p0=lin[0]-quad[0]; p0=vec3(dot(p0,U)/u,dot(p0,V)/v,dot(p0,W));
p1=lin[1]-quad[0]; p1=vec3(dot(p1,U)/u,dot(p1,V)/v,dot(p1,W));
dp=p1-p0;
// test if crossing the plane
if (fabs(dp.z)<1e-10) return false;
t=-p0.z/dp.z;
p=p0+(t*dp);
// test inside 2D quad (rectangle)
if ((p.x<0.0)||(p.x>1.0)) return false;
if ((p.y<0.0)||(p.y>1.0)) return false;
// inside line
if ((t<0.0)||(t>1.0)) return false;
return true;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
bool collideQuadQuad(vec3 *quad0,vec3 *quad1) // return if quad0[4] is colliding quad1[4]
{
int i;
vec3 l[2];
// lines vs. quads
for (i=0;QUAD_lin[i]>=0;)
{
l[0]=quad0[QUAD_lin[i]]; i++;
l[1]=quad0[QUAD_lin[i]]; i++;
if (collideLineQuad(l,quad1)) return true;
}
for (i=0;QUAD_lin[i]>=0;)
{
l[0]=quad1[QUAD_lin[i]]; i++;
l[1]=quad1[QUAD_lin[i]]; i++;
if (collideLineQuad(l,quad0)) return true;
}
// ToDo coplanar quads tests (not needed for AABB test)
return false;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
bool collideAABBQuad(vec3 *aabb,vec3 *quad) // return if aabb[8] is colliding quad[4]
{
int i;
vec3 q[4],n,p;
// test all AABB faces (rectangle) for intersection with quad (rectangle)
for (i=0;AABB_fac[i]>=0;)
{
q[0]=aabb[AABB_fac[i]]; i++;
q[1]=aabb[AABB_fac[i]]; i++;
q[2]=aabb[AABB_fac[i]]; i++;
q[3]=aabb[AABB_fac[i]]; i++;
if (collideQuadQuad(q,quad)) return true;
}
// test if one point of quad is fully inside AABB
for (i=0;AABB_fac[i]>=0;i+=4)
{
n=cross(aabb[AABB_fac[i+1]]-aabb[AABB_fac[i+0]],
aabb[AABB_fac[i+2]]-aabb[AABB_fac[i+1]]);
if (dot(n,quad[0]-aabb[AABB_fac[i+0]])>0.0) return false;
}
return true;
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
And here the usage (during rendering):
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
int i;
float m[16];
mat4 m0,m1;
vec4 v4;
float aspect=float(xs)/float(ys);
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
gluPerspective(60.0/aspect,aspect,0.1,20.0);
glMatrixMode(GL_TEXTURE);
glLoadIdentity();
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glLoadIdentity();
static float anim=180.0; anim+=0.1; if (anim>=360.0) anim-=360.0;
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
glDisable(GL_CULL_FACE);
vec3 line[2],quad[4],aabb[8]; // 3D vectors
get_perspective_znear(quad);
// store view matrix for latter
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glGetFloatv(GL_MODELVIEW_MATRIX,m);
m0=mat4(m[0],m[1],m[2],m[3],m[4],m[5],m[6],m[7],m[8],m[9],m[10],m[11],m[12],m[13],m[14],m[15]);
m0=inverse(m0);
// <<-- here should be for start that loop through your toruses
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glPushMatrix();
// set/animate torus position
glTranslatef(0.3,0.3,3.5*(-1.0-cos(anim)));
glRotatef(+75.0,0.5,0.5,0.0);
// get actual matrix and convert it to the change
glGetFloatv(GL_MODELVIEW_MATRIX,m);
m1=m0*mat4(m[0],m[1],m[2],m[3],m[4],m[5],m[6],m[7],m[8],m[9],m[10],m[11],m[12],m[13],m[14],m[15]);
// render torus and compute its AABB
glEnable(GL_LIGHTING);
glEnable(GL_LIGHT0);
glColor3f(1.0,1.0,1.0);
glutSolidTorus(0.1,0.5,36,36);
AABBSolidTorus(aabb,0.1,0.5);
glDisable(GL_LIGHT0);
glDisable(GL_LIGHTING);
// convert AABB to the same coordinates as quad
for (i=0;i<8;i++) aabb[i]=(m1*vec4(aabb[i],1.0)).xyz;
// restore original view matrix
glPopMatrix();
// render wireframe AABB
glColor3f(0.0,1.0,0.0);
glBegin(GL_LINES);
for (i=0;AABB_lin[i]>=0;i++)
glVertex3fv(aabb[AABB_lin[i]].dat);
glEnd();
/*
// render filled AABB for debug
glBegin(GL_QUADS);
for (i=0;AABB_fac[i]>=0;i++)
glVertex3fv(aabb[AABB_fac[i]].dat);
glEnd();
// render quad for debug
glBegin(GL_QUADS);
glColor3f(1.0,1.0,1.0);
for (i=0;QUAD_fac[i]>=0;i++)
glVertex3fv(quad[QUAD_fac[i]].dat);
glEnd();
*/
// render X on colision
if (collideAABBQuad(aabb,quad))
{
glColor3f(1.0,0.0,0.0);
glBegin(GL_LINES);
glVertex3fv(quad[0].dat);
glVertex3fv(quad[2].dat);
glVertex3fv(quad[1].dat);
glVertex3fv(quad[3].dat);
glEnd();
}
// <<-- here should be end of the for that loop through your toruses
glFlush();
SwapBuffers(hdc);
just ignore the GLUT solid torus function as you already got it ... Here preview:
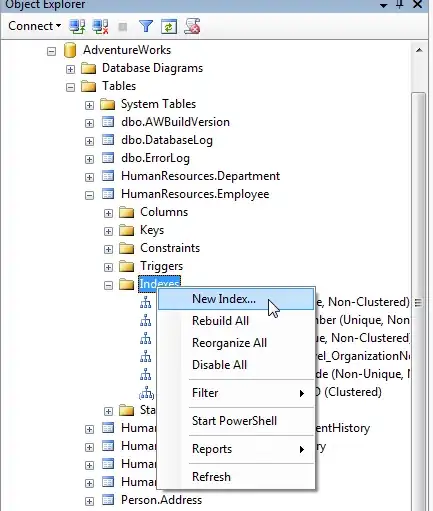
The red cross indicates collision with screen ...